De Architectura, or On Architecture, is a treatise written between 30 and 15 BC by the Roman architect Marcus Vitruvius Pollio.
A Model Through Time
As it is the only treatise on architecture left from its time, De Architectura is the first book on architectural theory. It’s based on Vitruvius’ own experience, as well as on theoretical works by famous Greek architects. Moreover, the work covers almost every aspect of architecture. However, it has limits since it tells primarily about Greek models, from which Roman architecture soon abandoned to serve the needs of their new empire.

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/a79003e4-f71d-46bf-bbce-6dc5fd51c651 by Creator:Fra Giovanni Giocondo da VeronaCreator:Fra Giovanni Giocondo da VeronaCreator:Giovanni TaccuinoCreator:Marcus Pollio Vitruvius

Image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/De_architectura#/media/File:De_architectura.jpg
De Architectura describes urban planning and architecture in general. The treatise is divided into 10 books: building materials; the building of temples and the use of Greek orders; public buildings (theaters, baths); private buildings; floors and moldings; hydraulics; clocks, measurements, and astronomy; civil and military engines.
However, the book also discusses art, natural history, and building technology. Additionally, it is purely Hellenistic in nature, as Vitruvius did not accept modern architecture.
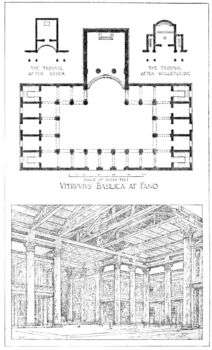
Image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitruvius#/media/File:Vitruvius_the_Ten_Books_on_Architecture_Basilica_at_Fano.png
Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/fc7153d2-9f03-431d-ba32-1f893926dc63
The principles of Good Architecture
There are three principles of good architecture proclaimed by Vitruvius in De Architectura:
- Firmatis (Strength) – Should stand sturdy and in good condition
- Utilitas (Utility) – Should be useful and functional for the people who use it
- Venustatis (Beauty) – Should delight and lift people’s spirits
The triad of characteristics, outlined in Book III, derives partially from Latin rhetoric (through Cicero and Varro) and has guided architects for centuries. The Roman author also described his research on the architect’s qualifications (Book I), and the types of architectural drawing.

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/e3edb3a9-2188-4599-8e09-77ee61821e05 by Creator:Sangallo familyCreator:Marcus Pollio Vitruvius
Buildings, Architecture and Human Proportions
De Architectura describes the various devices used for engineering structures, such as hoists, cranes, and pulleys, as well as military vehicles such as catapults, ballistae and siege machines. Inthe ten chapters, Vitruvius discusses the construction of a sundial and water clock and the use of an aeolipile (the first steam engine) as an experiment to demonstrate the nature of the movement of atmospheric air (wind). In Book III, Vitruvius also studied the proportions of man, and his principles are present in the famous drawing by Leonardo da Vinci (Homo Vitruvianus, “Vitruvian Man”).

Image source: https://search.creativecommons.org/photos/54e83f81-c66b-4cc1-b4ba-f116a41eb2f2 by Ralph Buckley
Info sources:
https://clinicalarchitecture.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki
https://www.britannica.com
